Projects: Collaborate.Health
Rheumatic Heart Disease in Malawi
Tracking and Treating Rheumatic Heart Disease Patients in Malawi
Overview
A high prevalence of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in Malawi leads to considerable cardiac morbidity and mortality. Exposure to streptococcal pharyngitis can lead to acute rheumatic fever resulting in severe cardiac valve damage.
Context
In 2018, the World Health Organization unanimously adopted a Global Resolution on Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD) at the World Health Assembly in Geneva, Switzerland acknowledging for the first time that RHD was a global health priority on a global scale. Recommendations and goals for RHD included:
- Strengthening data collection and knowledge of RHD prevalence in endemic countries
- Ensuring affordable and reliable access to technologies and medicine
- Monitoring efforts for the prevention and control of RHD
- Supporting and facilitate timely, affordable and reliable access to existing and new cost-effective medicines and technologies for the prevention and control of RHD.
Challenge
How can community health workers in Malawi keep an accurate, up-to-date record of children who have rheumatic heart disease (RHD) and connect them with the appropriate resources to ensure that they do not develop further strep throat or more severe chronic disease?
Solution
Develop a mobile application to register RHD patients and improve surveillance of rheumatic heart disease among youth in rural and urban Malawi while ensuring that registered youth receive the recommended monthly injections of benzathine penicillin to prevent further strep throat and RHD disease progression.
Results
Using mobile phones with the CommCare Application will allow health workers at Kamuzu Central Hospital and health workers at local clinics to:
- Enter information for patients who have been diagnosed with rheumatic heart disease and who have been given a benzathine penicillin regimen (BPG) (1 given in person, 2 for the next two months)
- Determine if patients are stable enough for a follow-up in 3 months. If not patients will be following up every month with clinician
- Keep track of patients who are due for another benzathine penicillin injection by including a built-in calculation that estimates when patients are in need of another injection (once 28 days has passed)
- A label will be included to remind local health care workers to reach out to patients in need of another injection
- Take a note of whether or not patients are late for their injection and note how many days late; take a note of adherence
- Communicate among each other when patients are being diagnosed with rheumatic heart disease and when benzathine penicillin injections are being administered
- Counsel patients on RHD treatment plan
Project Timeline
This project took six months to complete from kick-off meeting to presentation of final deliverables. Click the button below for a detailed timeline.
View Project TimelineProject Team
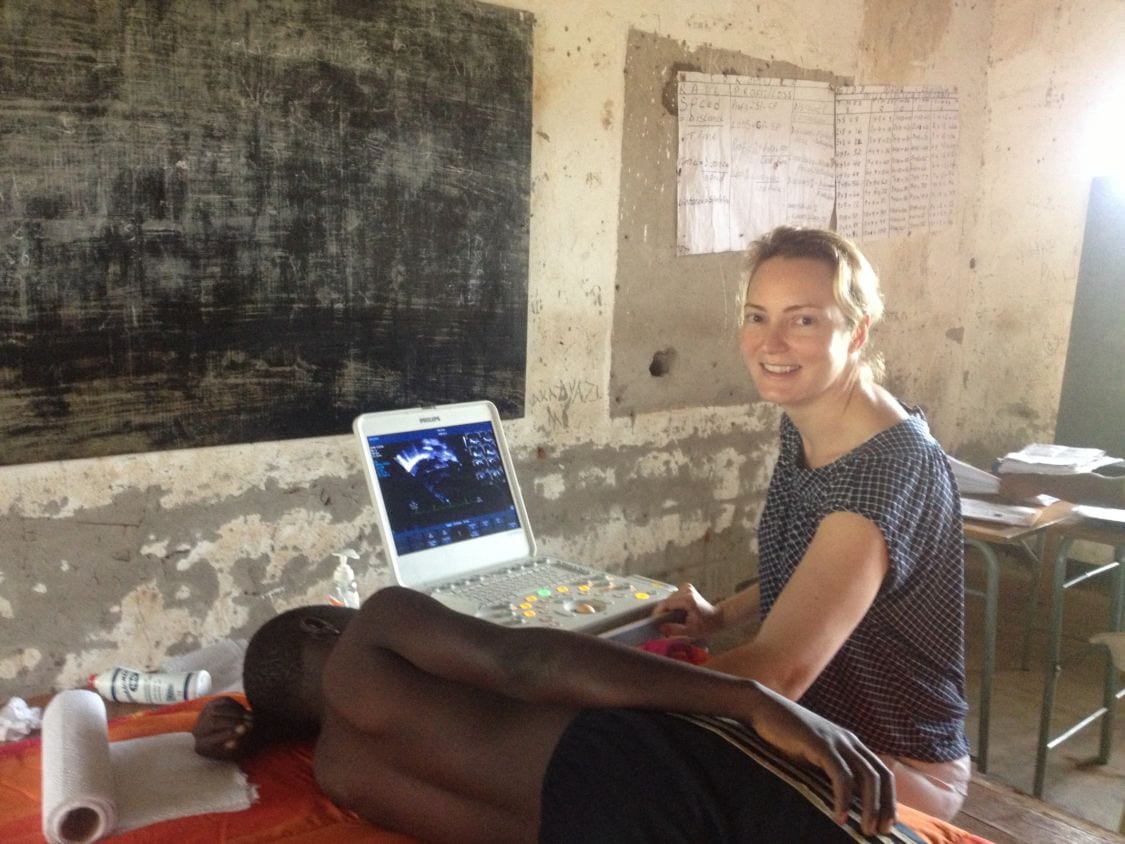


Client-Mentor Spotlight
Amy Sanyahumbi, MD
Amy Sanyahumbi, MD is an Assistant Professor of Pediatric Cardiology at Texas Children’s / Baylor College of Medicine. She is currently based in Lilongwe, Malawi, where she leads an NIH K – Award research program to improve adherence to benzathine penicillin among Malawian children with rheumatic heart disease. She also runs the pediatric cardiology clinic at Kamuzu Central Hospital. After completing her pediatric cardiology fellowship at Children’s National Medical Center in Washington, DC, she returned to Malawi to complete an NIH Fogarty Global Clinical Research Fellowship. Amy subsequently accepted a position with the Baylor Pediatric Cardiology Department after her Fogarty fellowship, and continues her work in global pediatric cardiology with a focus on rheumatic heart disease.
Rheumatic Heart Disease RED Presentation
RHD RED Consulting Slide Deck and Application User's Guide
For more information about Rheumatic Heart Disease, visit RHD Action, an organization heading up a global movement to reduce the burden of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in vulnerable populations of all ages throughout the world.